News
- Science Stories
- Highlights
- Looking for collaboration
- Helpful links
- Logos
Science Stories
It is our mission being accomplished. Since 1994, the BIAL Foundation has approved for funding 946 projects, involving around 1900 researchers from 31 countries. There are three decades of support to Scientific Research Projects oriented toward the neurophysiological and mental study of the human being, in the areas of Psychophysiology and Parapsychology.
Discover the stories behind the science.
Science Stories
Do illusory beliefs drive people away from medicine?
The stronger the belief in pseudoscientific ideas, the greater the distrust in conventional medicine and tendency to seek unvalidated therapies, a study shows.

What leads some mothers to perinatal depression?
A pioneering study followed mothers with perinatal depression and concluded that sensitivity can increase the risk, but partner support has a protective effect.

Do we feel less moral responsibility when following orders?
Study confirms that the perception of being the author of our actions decreases when we follow orders.

Which factors influence dream recall?
Research revealed the main factors that determine dream recall: attitude towards dreams, tendency to mind wandering, and sleep patterns.

How does the brain respond to positive and negative stimuli?
Study demonstrates the brain's ability to constantly reclassify external stimuli based on previous experiences and adapt to new situations.

Are people who believe in the paranormal more vulnerable to stress?
A study of 3084 participants evaluated whether two types of belief in the paranormal might be associated with different levels of perceived stress.

Do we perceive the weight of our body parts and the weight of objects differently?
According to Newton’s law, weight is given by the product of its mass and gravity. How does the brain determine the weight of objects and body parts?

Does the combination of psychedelics and meditation enhance mystical experiences?
Researchers assessed whether combining psychedelics with meditation increases mindfulness, compassion, insight, and mystical-type transcendence to a higher degree than meditation with a placebo.

Health professionals' responses to stress in critical care scenarios and the risk of burnout
A study assessed the psychobiological functioning of 27 Pre-Hospital Emergency Medical doctors and paramedics, stressing the importance of recovery periods.

Are psi researchers more like lay believers or sceptics?
A study shows that academics who work with psi differ from lay psi individuals, but not from sceptics, in actively open-minded thinking.
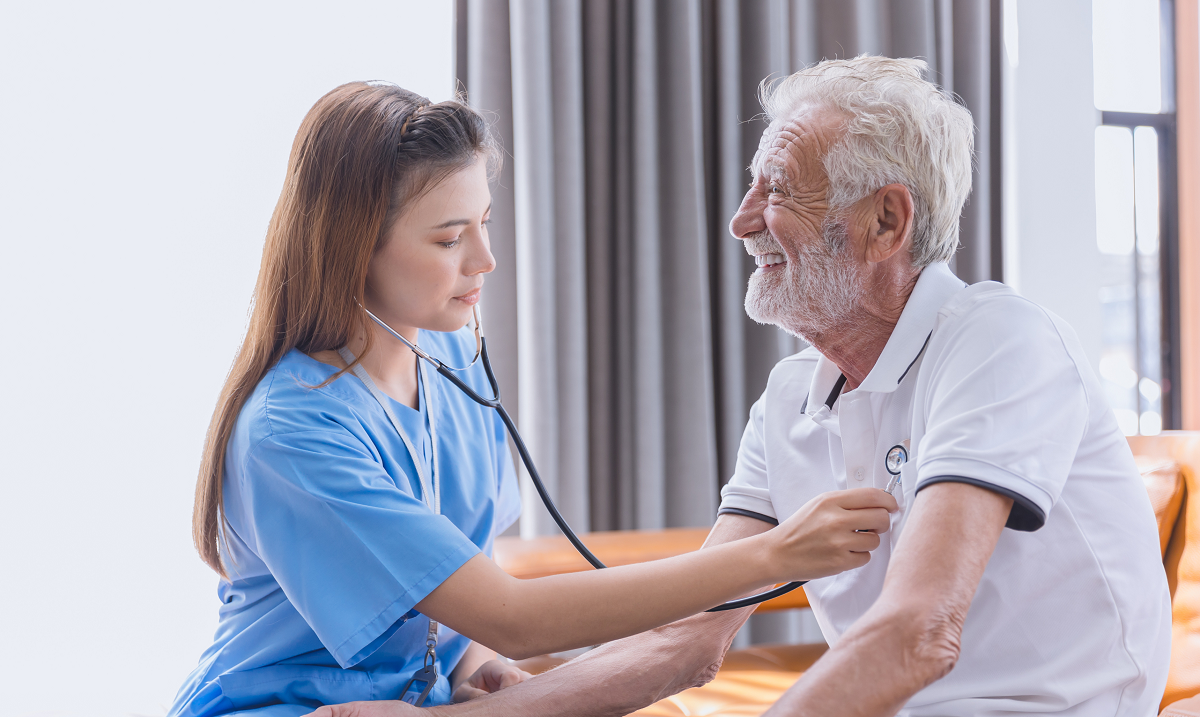

Could the healthcare provider's nonverbal behaviour modulate pain reports and placebo effects?
The effects of the nonverbal behaviour of healthcare providers on pain reports and placebo effects may differ in healthy males and females.
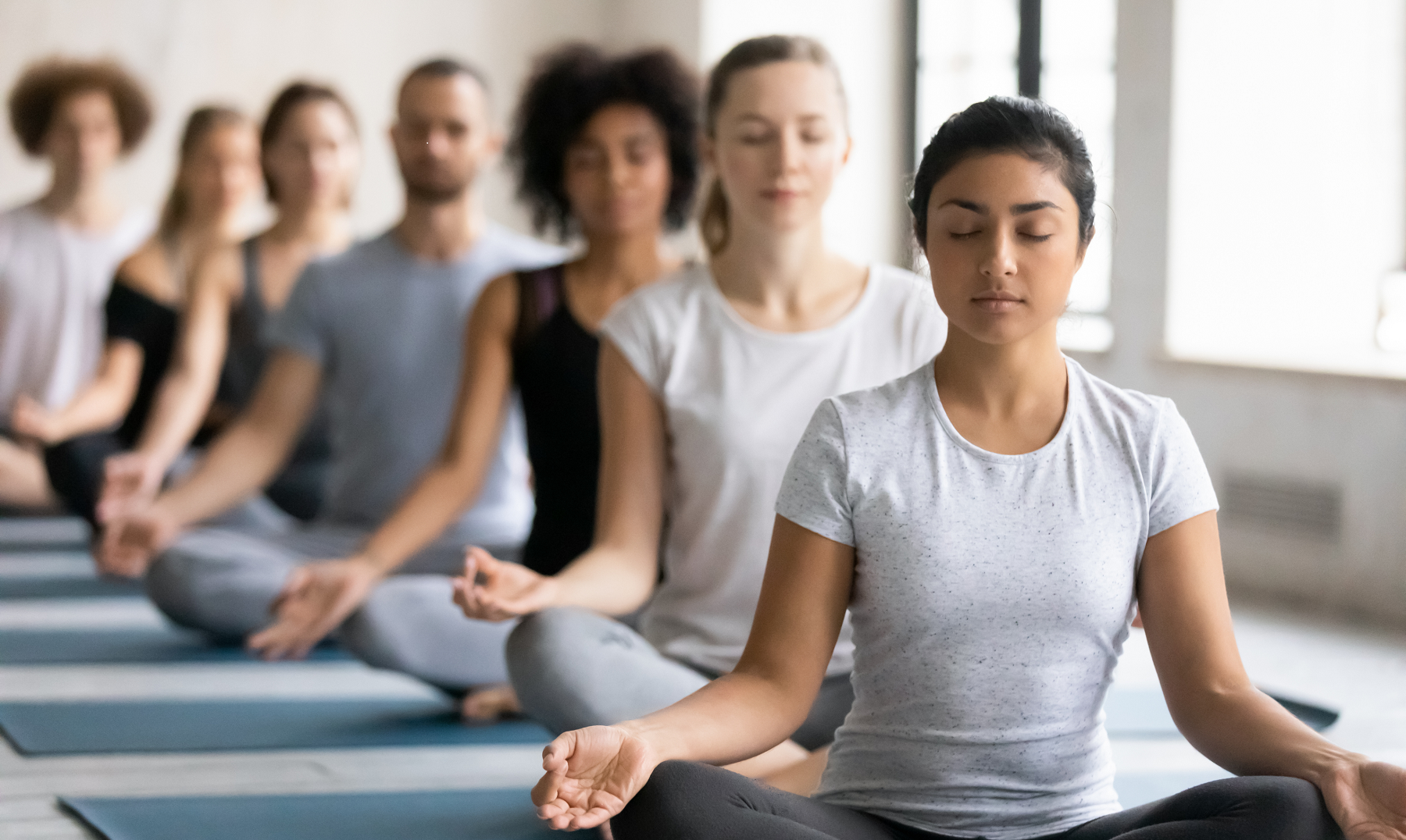

To what extent do the boundaries of our body seem to fade during focused-attention meditation?
An experimental study revealed that a 15-minute focused-attention meditation session blurred the boundary between the self and the environment.
News

How does the brain turn what it sees into action?
A study reveals the plasticity of neural pathways and how the brain repurposes motor networks to learn new associations, a testament to its adaptability.

Did you know it’s possible to study awe in the human brain?
The SUBRAIN project aims to understand the brain mechanisms underlying the emotion of awe, defined as a profound feeling of wonder in response to something sublime.

Do unconventional beliefs help give life meaning?
A study suggests that unconventional beliefs may reflect alternative and psychologically rich ways of attributing meaning to existence.

Nuno Grande Doctoral Scholarship gains national scope and awards three grants per edition
BDNG will have national coverage, allowing PhD students in Fundamental Health Sciences from Portuguese universities to apply.

BIAL Award in Biomedicine 2025: last call for nominations
The nominations for the 4th edition of the BIAL Foundation international award, the BIAL Award in Biomedicine 2025, close on June 30.

The Proceedings of the 14th Symposium of the BIAL Foundation is now available
The BIAL Foundation has just published the Proceedings of the 14th "Behind and Beyond the Brain" Symposium on the theme “Creativity”.
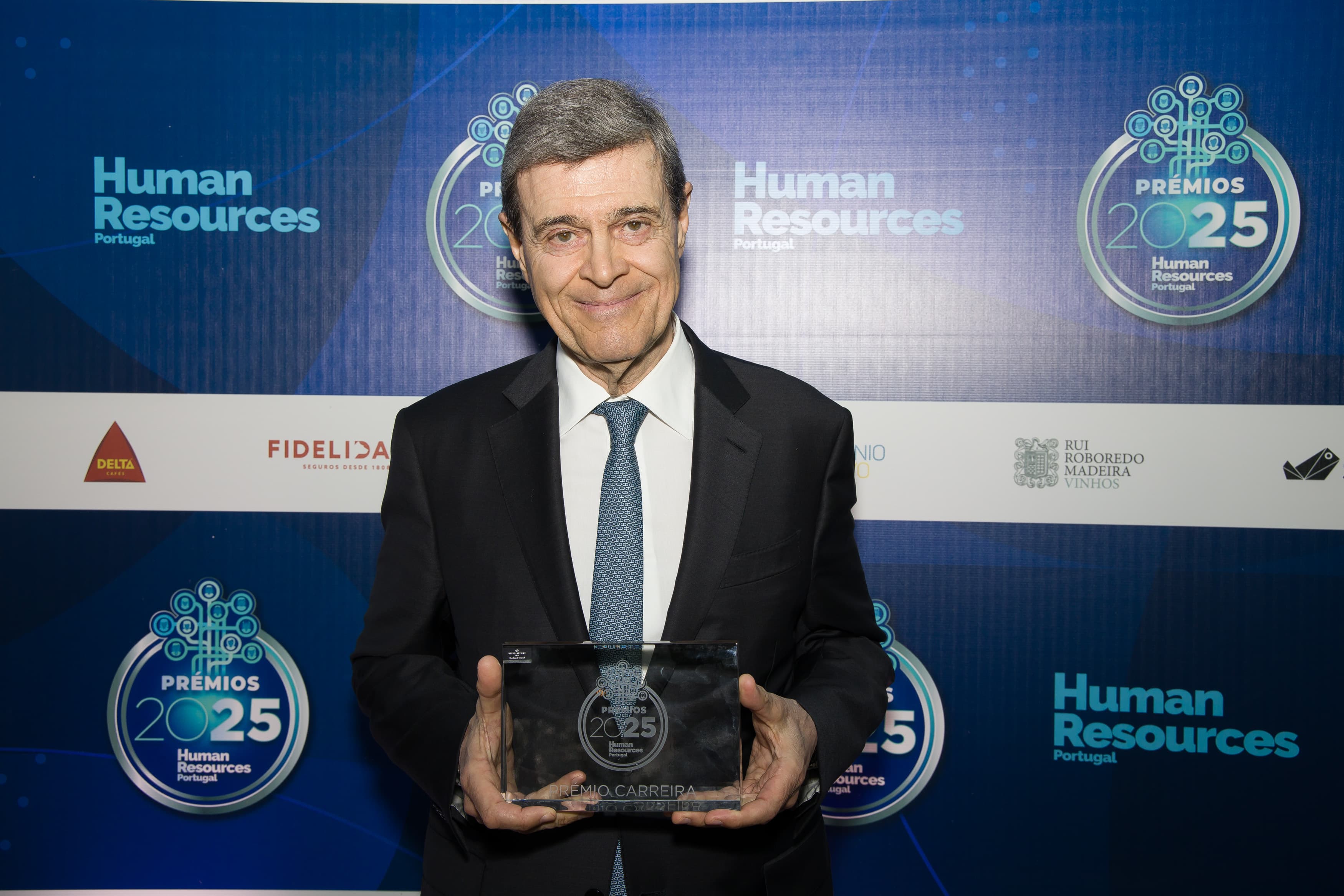

Luís Portela honoured with Career Award by Human Resources
The chairman of the BIAL Foundation, Luís Portela, was honoured with the Career Award by Human Resources Portugal.

How does the brain track the rhythm of music?
A study reinforces the idea that music, although culturally rich and diverse, is grounded in mechanisms deeply rooted in our biology.

Illusory beliefs: An invisible obstacle to medicine?
A study shows that the stronger the belief in pseudoscientific ideas, the greater the distrust in conventional medicine.

Why are some mothers more vulnerable to perinatal depression?
A study tracked the trajectory of perinatal depression at four distinct points – in late pregnancy, and at 3, 6, and 9 months postpartum.

Maria de Sousa Award 2025: applications are open until May 31
The Maria de Sousa Award aims to award and support young Portuguese researchers, aged 35 or under, with scientific projects in Health Sciences.

The brain captures emotions before we are aware – but how and with what effect?
A study supported by the BIAL Foundation shows that faces with fearful expressions are detected more quickly than those with angry or happy expressions.
Looking for collaboration

The quest of physiological markers for the experience of pain
Researcher: Elia Valentini - Department of Psychology & Centre for Brain Science, University of Essex Summary: The aim of this project is to improve measurement of the human experience of pain by investigating a combination of psychophysical and physiological responses during mild noxious stimulation. More specifically, we want to investigate how sensitive and specific to pain the brain oscillatory responses are. We use EEG as the main technique, but we are keen to collaborate with neuroscientists using fMRI, autonomic measures and brain stimulation as well as with computational neuroscientists. A clinical collaborator would also be very much welcome.

EEG investigation of hypnosis and decision-making
Researcher: Rinaldo Livio Perri - University Niccolò Cusano Rome, Italy Summary: I work in the field of hypnosis and cognitive neuroscience. In particular, I adopt the event-related potentials (ERPs) to investigate the effect of the hypnotic suggestions on sensory processing and cognitive performance. I am an expert in decision-making and proactive brain processes before the stimulus administration (e.g., the perceptual, prefrontal and premotor readiness during the expectancy stage). I could help colleagues to properly analyze the ERP signal in the pre-stimulus stage of processing. Also, I would be happy to share my EEG data for re-analyzing them in the frequency domain (e.g., wavelet or coherence analysis in the hypnosis research). Feel free to contact me for any question! More information on my papers: https://scholar.google.it/citations?user=-8e_V64AAAAJ&hl=it Possible collaborations: neuroscientist with experience in the EEG frequency analysis Email: perri.rinaldo@gmail.com

Transparent Psi Project - looking for collaborators
Summary: We are running a fully transparent, expert consensus-base multilab replication of Bem’s (2011) experiment 1. The project features state of the art methods to maximize transparency and study integrity. The study involves a computerized experiment taking about 20 minutes per session. Group testing is possible in a computer lab, no specialized equipment needed. Labs are expected to recruit at least 100 participants. Participants will be exposed to images with explicit erotic/sexual content in the experiment. No financial compensation is required for the participants. Data collection is expected to take place in the 2020 fall semester. Every material is provided for ethics/IRB submissions and data collection in English (translation of materials might be necessary by the collaborators). The study is pre-registered and the manuscript is accepted in principle for publication in the journal Royal Society Open Science. All collaborators who meet the minimum sample size criterion will get authorship on this paper reporting the results of the replication study. More information in the preprint: https://psyarxiv.com/uwk7y/ Indicate interest in the collaboration via the following form: https://tinyurl.com/tpp-labs With any question contact the lead investigator: Dr. Zoltan Kekecs, kekecs.zoltan@gmail.com

Cognitive control and learning
Researcher: Ignacio Obeso, Ph.D. / CINAC - HM Puerta del Sur Summary: The aim of our projects is to understand the behavioral and neural mechanisms used to learn how humans establish adaptive behaviour in changing contexts. More specifically, we want to decipher how stopping abilities are initially learned and later executed under automatic control. We use task-related fMRI, brain stimulation and clinical models to test our predictions in laboratory settings as well as online home-based paradigms. Possible collaborations: computational scientist Email contact: i.obesomartin@gmail.com https://iobesomartin.wixsite.com/cognitivecontrol
Find here some links to other Foundations, Organizations, Societies and more that you might be interested in.
- BrainFacts.org
- Cognitive Neuroscience Society
- Dana Foundation
- European Brain Council
- European Society for Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience (ESCAN)
- Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS)
- Human Brain Project
- IANDS International Association for Near-Death Studies
- Institut Métapsychique International (IMI)
- Instituto de Psicologia Paranormal
- International Behavioral Neuroscience Society (IBNS)
- International Brain Research Organization
- IONS Institute of Noetic Sciences
- Kavli Foundation
- Koestler Parapsychology Unit
- Open Sciences
- Organization for Human Brain Mapping (OHBM)
- Parapsychological Association
- Psi Encyclopedia
- Rhine Research Center
- Sociedade Portuguesa de Neurociências
- Sociedade Portuguesa de Neurologia
- Society for Neuroscience
- Society for Psychical Research
- Society for Scientific Exploration (SSE)
- World Federation of Neurology






